Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology has garnered significant interest in the robotic vision community over the past few decades. The rapid development of SLAM technology has resulted in its widespread application across various fields, including autonomous driving, robot navigation, and virtual reality. Although SLAM, especially Visual-Inertial SLAM (VI-SLAM), has made substantial progress, most classic algorithms in this field are designed based on the assumption that the observed scene is static. In complex real-world environments, the presence of dynamic objects such as pedestrians and vehicles can seriously affect the robustness and accuracy of such systems. Event cameras, recently introduced motion-sensitive biomimetic sensors, efficiently capture scene changes (referred to as "events") with high temporal resolution, offering new opportunities to enhance VI-SLAM performance in dynamic environments. Integrating this kind of innovative sensors, we propose the first event-enhanced Visual-Inertial SLAM framework specifically designed for dynamic environments, termed E2-VINS.
Overall Framwork
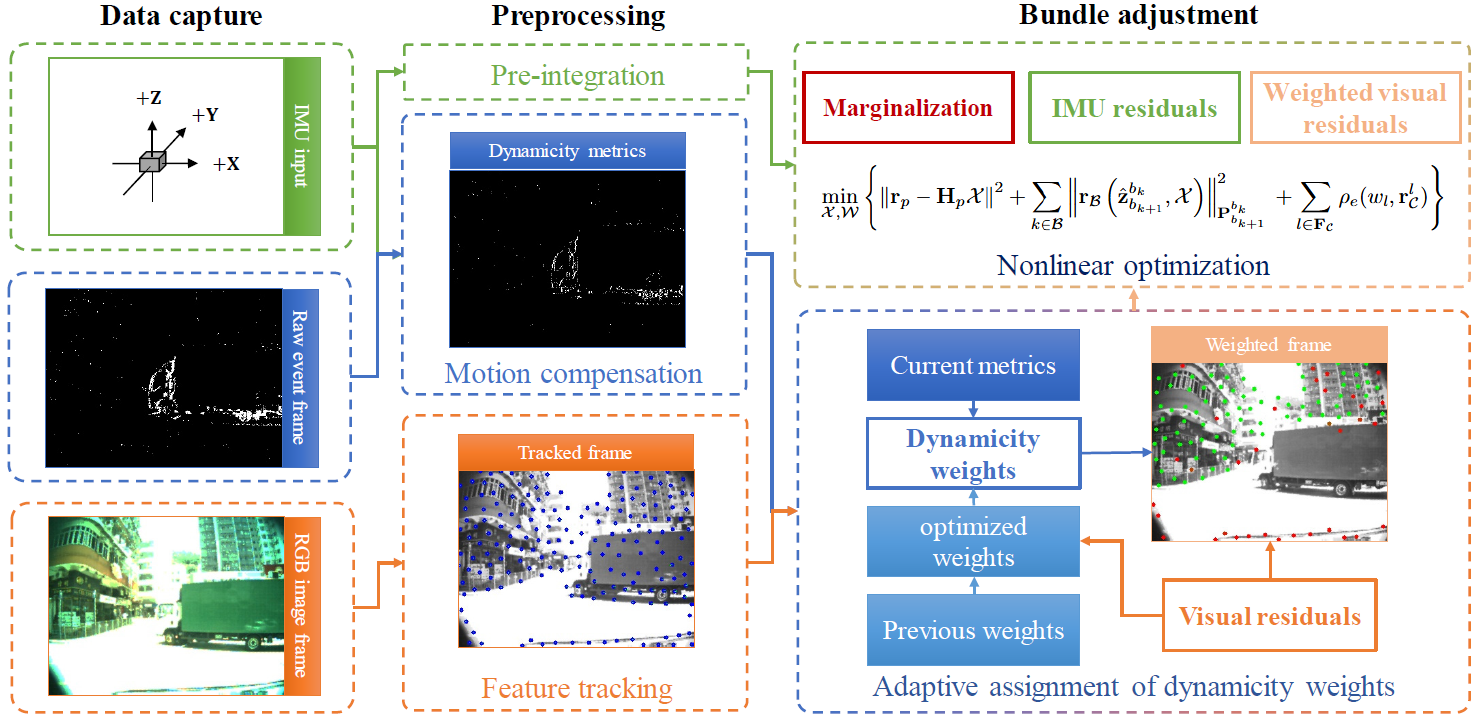
The overall pipeline of our proposed E2-VINS system is shown as Figure 1. "Preprocessing" involves IMU pre-integration, event motion compensation, and feature tracking of RGB frames. Compensated events are used to generate event-based dynamicity metrics that measure the dynamicity of each pixel. Based on these metrics, weights for visual residuals of different pixels are adaptively assigned, referred to as dynamicity weights. Finally, E2-VINS optimizes the system state (camera poses and map points) and dynamicity weights.
Performances
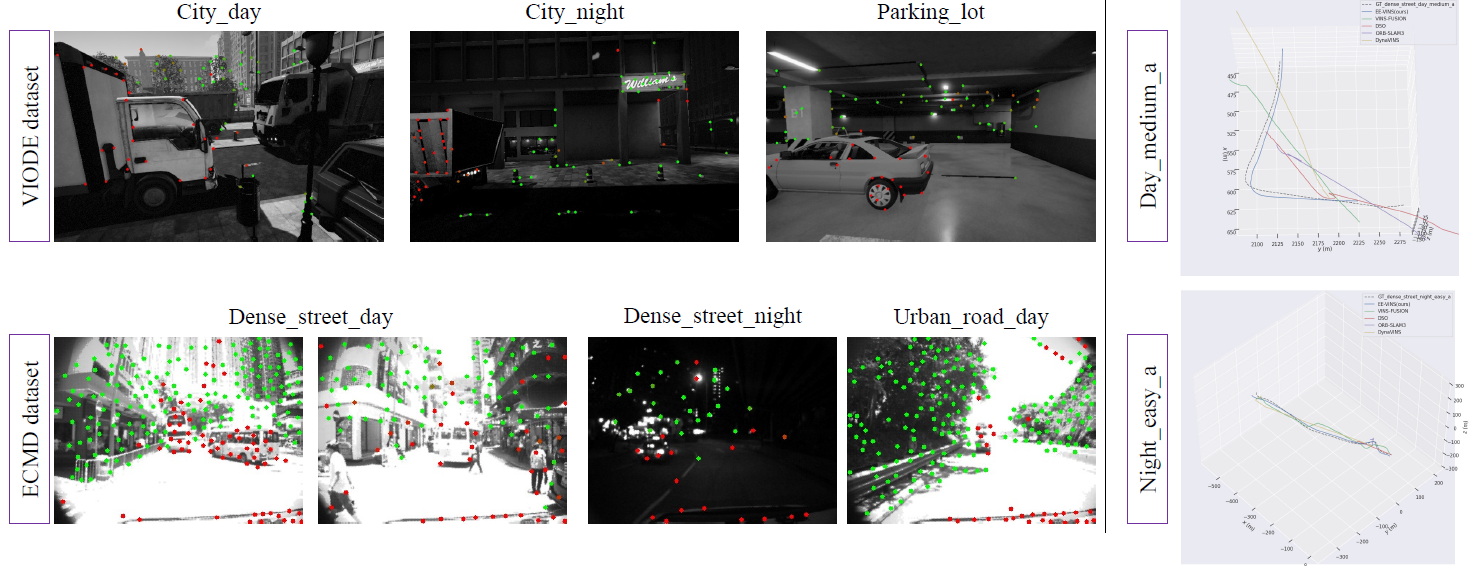
- Qualitative Results

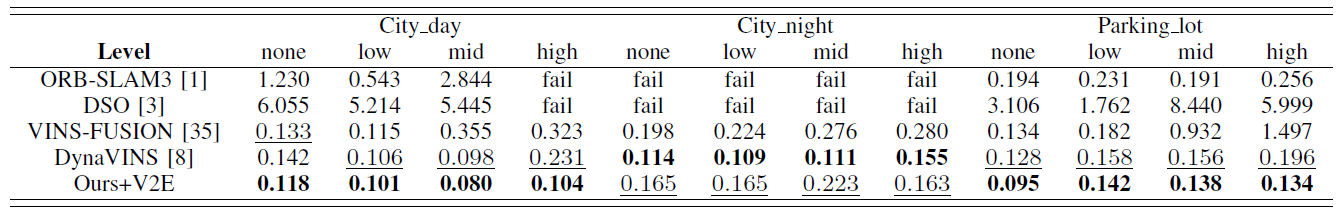
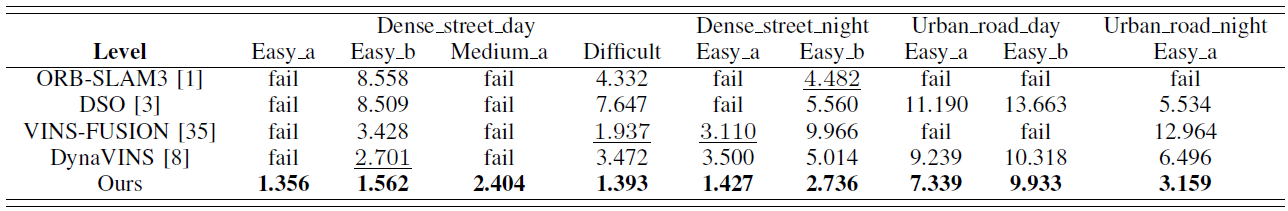
- Quantitative Results
Source Codes